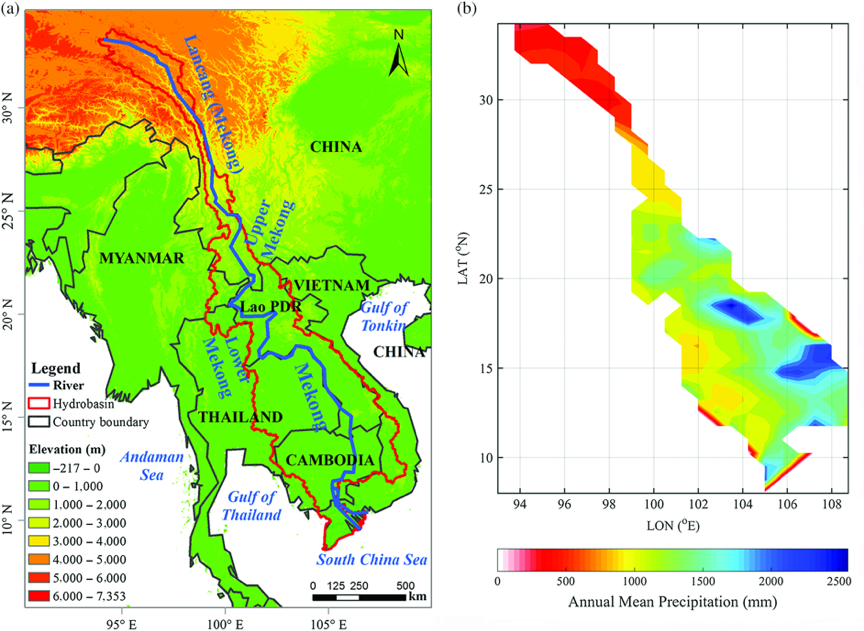
Accurate precipitation data is the basis of hydro-climatological research. As a river basin with a large population and one of the largest inland fishery industries in the world, the dynamic change of water resources is of great significance. In fact, poor ground observation data in the Mekong Basin prevented accurate analysis of precipitation dynamics in the region. With the development of science and technology, satellites and reanalysis methods can provide accurate spatial-temporal resolution of precipitation data. This makes up for the lack of observational data, especially in remote areas where there is a lack of observations. At present, many studies have evaluated satellite and reanalyzed precipitation data sets on different spatial scales. However, for the Mekong River Basin, there has been no study on the reliability of the latest multi-source high-resolution grid precipitation data sets (satellite and reanalysis precipitation data) for spatial-temporal change simulation.
Therefore, Gothenburg University of earth sciences Deliang Chen group in Asia - high resolution observation precipitation data integration comparative assessment of water precipitation products (APHRODITE), for high resolution satellite (PERSIANN - CDR, TRMM) and reanalysis precipitation data set (CFSR, ERA - Interim, and MERRA2) in the reliability of the Mekong river basin were evaluated. APHRODITE was chosen as the comparative reference because it was the only long-term, celestial precipitation product in Asia, and it integrated the largest amount of ground observation data, adopts improved quality control method and precipitation terrain correction. It was not only regarded as a "ground observation data" by many related studies, but also proved to be helpful for the simulation of the mainstream runoff of the Mekong river as the input of precipitation products.
The results showed that most of the assessment data sets could capture the main climatological characteristics of rainfall in the Mekong river basin during the study period (1998-2007). In general, the satellite data (TRMM and PERSIANN-CDR) showed higher reliability than the reanalysis products in the whole Mekong river basin on the spatial-temporal scale. The performance of TRMM was better than PERSIANN-CDR. In the reanalysis products, MERRA2 was relatively reliable in terms of time variability, but it underestimated the precipitation to a certain extent. Both the CFSR and the era-interim governments overestimated rainfall. In addition, CFSR had certain advantages in capturing the spatial changes of precipitation, while the simulation of era-interim for daily precipitation probability distribution was relatively good.
Because of the spatiotemporal heterogeneity of precipitation and its key role in human activities, it was of great significance to grasp the spatiotemporal variation of precipitation in the Mekong River Basin. For the poor ground observation status of the Mekong River Basin, satellite and reanalysis of precipitation data provided an alternative solution to precipitation data with good spatial and temporal resolution. The novelty of this study was that it was the first time to comprehensively evaluated the reliability of satellite and reanalyzed the grid precipitation data set with high spatial and temporal resolution in order to help improve the precipitation evaluation in the region in the future.
The research results were published in the International Journal of Climatology by doctoral student Aifang Chen as the first author and professor Deliang Chen as the corresponding author. Strategic leading science and technology projects, Chinese academy of sciences: extensive environmental change and the third pole green silk road construction (XDA20060401), China's national study foundation, China national natural science fund committee (91537210), Sweden STINT (CH2015-6226), the European Union's horizon, 2020 research and innovation plan MARIE SK Ł ODOWSKA - CURIE ACTIONS (703733), etc.
Paper link: https://rmets.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/joc.5670